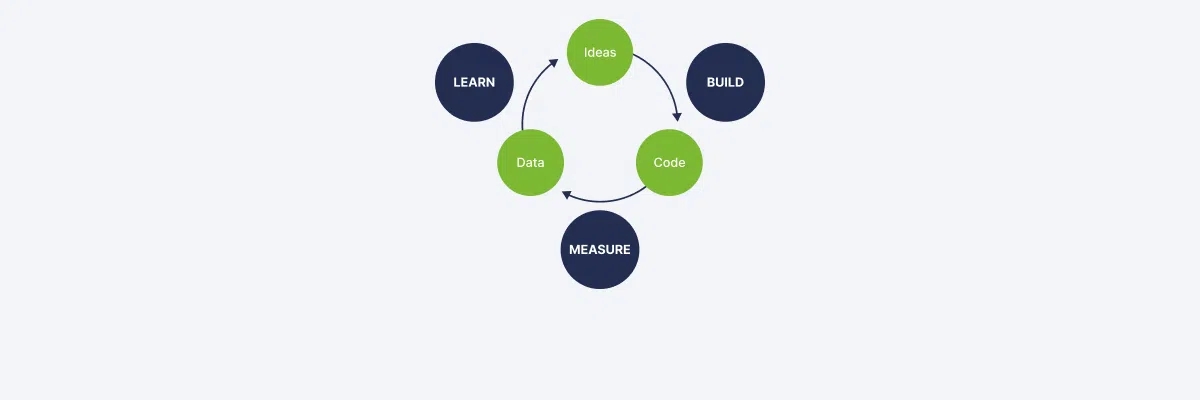
Lean Startup Methodology Cycle: 4 Steps to Risk-Free Success
Over the past few years, the Lean Startup methodology has been in demand among entrepreneurs. This is a set of principles that guide startups when launching their product. The concept arose in response to the high risks involved in bringing a product to market. The lean startup methodology is designed to create an environment in which a startup can successfully launch, and numerous risks will be reduced.
Why has this technique gained its popularity? The fact is that 9 out of 10 new projects live for a maximum of a year, after which they fail. For small and medium-sized businesses, this situation is especially painful: if a large company, in case of failure, covers expenses with other sources of income and continues to work, then for small entrepreneurs this means the end of their activities. Therefore, it is vitaly important to calculate the possible risks and create conditions in which you can stay afloat. Below we will tell you what is remarkable about the lean startup methodology and what stages it consists of.
What is the Lean Startup Methodology?
The technique was first described by Eric Ries in his work The Lean Startup. It is based on the principles of Toyota's lean manufacturing model, which involves reducing waste and rationalizing the allocation of resources. The author notes that the uncontrolled loss of time, effort, and finances for an idea that is fundamentally unviable has negative consequences for a startup.
A startup has one significant feature - it requires an untested model to launch, in contrast to the already established lines of entrepreneurial activity. And if in the second case, to follow an established concept in order to succeed is enough, the path of a startup is to test an assumption. Therefore, it is optimal to isolate a hypothesis from the startup concept and conduct experiments to evaluate it. Customer reviews will help you understand whether you need to move in the chosen direction or choose another one.
In other words, the Lean Startup methodology emphasizes developing products or services that customers want, rather than building what the founder thinks customers want. This is possible due to validated learning, during which assumptions and hypotheses are tested.
Read also: Common Mistakes to Avoid when Building MVP
The 4 Steps of the Lean Startup Cycle
The cyclical nature of the methodology includes 4 mandatory stages, which are described in more detail below.
Business model template
The service and product development methodology instructs us to start by building a template where to answer important questions. When you answer, you make assumptions that you will later test. The template consists of 9 blocks with questions:
- Customer segment: who will value your product? Who is your ideal client?
- Value Proposition: What customer problems can you solve with the product? What is the value of the product for customers?
- Channels: how do you find customers? What channels are planned for communication? How are your competitors doing it? What channels are most effective? Do you know how your customers would like to be contacted?
- Customer Relationships: Is it impersonal and automated communication? Or is it a more personalized approach? How can you develop relationships with clients?
- Income streams: what tools are there for monetization? Do you plan to use the freemium model? What is the pricing policy? Do you have income now?
- Key Resources: What key assets are used to demonstrate value to customers? Is it intellectual property? Wat about human capital? Is it laborious to demonstrate a USP?
- Key Activities: What traits do you need to possess to demonstrate value? How to build relationships with clients? What about other companies?
- Key Partners: Who do you need to build partnerships with to demonstrate your USP? Is it necessary to build non-equity strategic alliances for this? Who are your suppliers/manufacturers/competitors?
- Costs: what is the most financially costly of the entire list of resources? What are the most important business model costs? Are these fixed or variable costs?
After studying all the blocks, we proceed to the second step.
Hypothesis Formation
At this stage, the best player divides the hypotheses into three categories of risk, borrowed from the concept of design thinking. From most to least important, these categories are:
- Desirability;
- Viability;
- Feasibility.
In the first category, risks are considered according to the attractiveness of the product, and the interest of customers in it. The viability of the model is based on finding solutions not only to customer problems, but also to actually attracting them, and assessing the profitability of the idea. The feasibility of an idea means the ability of a startup to create and launch products using available resources.
Minimum Viable Product (MVP)
MVP is a variant of a new product through which information is collected with the least effort. By creating an MVP, you define/create for yourself:
- product value;
- MVP type;
- landing page;
- explanatory video to introduce customers to the product.
Training
Software Development Services for Startups according to the lean cycle methodology completes the learning phase. In order for your product to meet market expectations, you must build customer feedback. This will help answer questions about:
- saving or modifying an existing model;
- adding/removing some features;
- the ability to charge for the use of the product;
- choice of advertising model for business or freemium.
Feedback from the client will help answer each question, which means confirming the hypothesis.
The Software Development Hub is dedicated to creating applications for startups. Guided by the principles of modern development methodologies, we will help you determine the tasks and value of the product, draw up a work plan, etc. Enterprise software development services are performed using modern technologies and tools, which allow you to create a functioning product.
Our portfolio includes medical information systems, e-Prescription systems, applications for tracking medicines with a QR scanner, medical ERP systems, etc.
Categories
Share
Need a project estimate?
Drop us a line, and we provide you with a qualified consultation.