Functional Decomposition: Aim, Procedure Description, Cases
What is Functional Decomposition? Business analysts employ a variety of techniques to carry out routine business analysis activities. A technique of functional decomposition is among the most popular. According to BABOK, “functional decomposition helps manage complexity and reduce uncertainty by breaking down processes, systems, functional areas, or deliverables into their simpler constituent parts and allowing each part to be analyzed independently.”
The term "functional decomposition" has its roots in mathematics, where it describes the act of dissecting all of the connections and connections that make up a functional relationship in order to recompose the original function. Fundamentally, functional decomposition simplifies a complex situation.
Additionally, business analysts may find it useful to break down processes or functions into smaller sub-functions in order to better understand how each one contributes to the achievement of the overall project's objective. Functional decomposition is a tool used by both large and small businesses to analyze projects and assess whether they are on track or whether there are smaller sub-functions that are slowing down the process.
Procedure of functional decomposition
Broadly, the process of functional decomposition appears as a complicated system divided into smaller, easier-to-understand components that may be independently examined, created, and developed through a process. A general outline of the functional decomposition procedure is provided below.
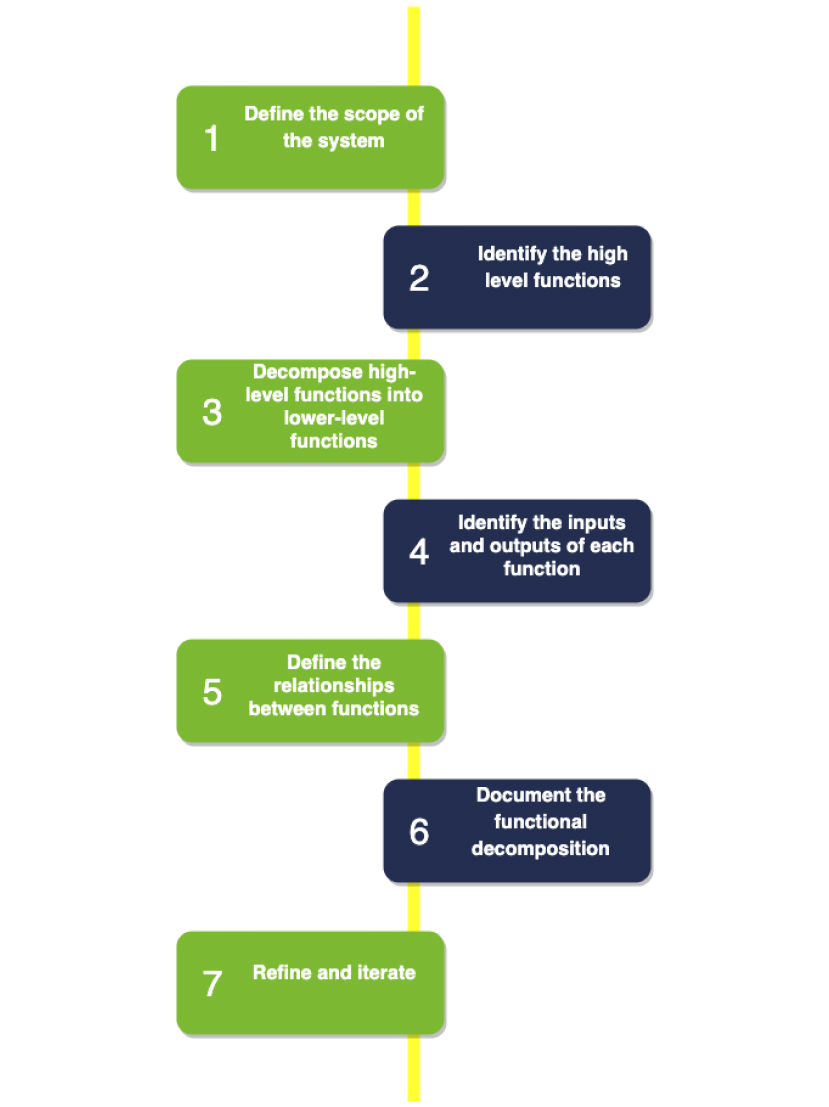
Figure 1 - Procedure of functional decomposition
- Define the scope of the system. The first stage is to decide what the system should and should not be able to perform. This makes it easier to create limits and restrictions.
- Identify the high-level functions of the system. The next stage is to determine the system's high-level functions. The primary tasks that the system has to complete in order to achieve its goals are represented by these functions.
- Decompose high-level functions into lower-level functions. The process of functional decomposition entails breaking down each high-level function into its simpler, more manageable lower-level counterparts. Up until the functionalities can be created and developed, this process is continued.
- Identify the inputs and outputs of each function. Determine the inputs and outputs that each function needs to do its mission. To make sure the function has accomplished its goals, the inputs should always be precisely stated, and the outputs must be described in enough detail.
- Define the relationships between functions. Determine the interconnections between the functions, such as which ones are reliant on others, which ones run concurrently, and which ones run in a sequential order. The optimum strategy to build the functions and integrate them into the system as a whole is determined by this knowledge.
- Document the functional decomposition. The outcomes of the functional decomposition process should be documented, together with a description of the functions, their inputs, outputs, and connections between them. The design and development of the system are based on this material.
- Refine and iterate. The functional decomposition procedure may be iterated and refined as needed to reach a clear and comprehensive knowledge of the system.
Read also: Managing Requirements Changes: Practical Case of Documentation
Functional decomposition diagrams
Business analysts can confirm and verify the results as well as utilize them for other activities thanks to the presentation of functional decomposition results. Simple text descriptions, hierarchical lists, explanations utilizing certain formal notations, and visual representations can all be used to represent the findings. Functional decomposition may be represented using a broad variety of diagramming approaches, including:
- Tree diagrams: show the hierarchical organization of tasks, activities, or outputs.
- Nested diagrams: show part-to-whole links between decomposition findings in a hierarchical fashion.
- Use case diagrams: show how a higher-level use case is broken down.
- Flow diagrams: show the outcomes of a process or function breakdown.
- State Transition diagrams: describe how an object behaves when it is in its composite state.
- Cause-and-effect diagrams: expand on the situations, circumstances, actions, and results that result in a complicated result or occurrence.
- Decision trees: describe a complicated decision's structure and probable consequences.
- Mind maps: categorize information and display it.
- Component diagrams: show how parts are connected to create bigger parts or software systems.
- Decision Model and Notation: examine the business logic and make sure it follows sound inferential and commercial principles.
But despite all this list, still the main tool for representing functional decomposition is functional decomposition diagram.
Real-life examples of functional decomposition
Functional decomposition is a commonly employed approach in several fields, including manufacturing, healthcare, IT, and finance. It aims to reduce complexity and make complex systems simpler to comprehend, design, and maintain. Companies may more effectively allocate resources, simplify procedures, and boost overall productivity and efficiency by breaking down a system into smaller tasks. This list offers case studies to demonstrate its use and real-world examples of functional decomposition in various sectors:
- Manufacturing: functional decomposition may be used in a manufacturing organization to divide the production process into more manageable operations. An automobile assembly line, for instance, may be broken down into smaller tasks like welding, painting, and assembly.
- Healthcare: the diagnosis and treatment processes in healthcare can use functional decomposition. A doctor, for instance, might break down the process of diagnosing a patient into smaller steps like gathering a patient's medical history, doing physical exams, and requesting lab testing.
- Retail: functional decomposition is used to assess intricate operations like inventory control and customer service and pinpoint opportunities for improvement.
- Banking: functional decomposition may be used to separate the loan processing process into smaller tasks like credit checking, reviewing the documents, and disbursing the loan.
- Education: in order to study intricate processes, such as curriculum creation and student evaluation, and suggest areas of concern, functional decomposition is utilized in education.
- Logistics: functional decomposition is employed to divide the supply chain process into more feasible processes, such as purchasing, shipping, warehousing, and distribution.
- Information Technology: in the development of the software, functional decomposition is frequently used to divide a project into smaller, more affordable activities. For instance, the creation of a new website may be broken down into more manageable tasks like design, coding, testing, and deployment.
An illustration of functional decomposition in IT projects can be demonstrated by one of the most common examples of the User management feature. User registration, login, password reset, and user profiles are only a few of the user-related operations that are covered by the breakdown. In addition, we take into account other factors including user roles and permissions, user activity logs, and user data privacy. In order to effectively manage users, provide security and privacy, and keep track of user activities, a comprehensive and user-friendly system is needed.
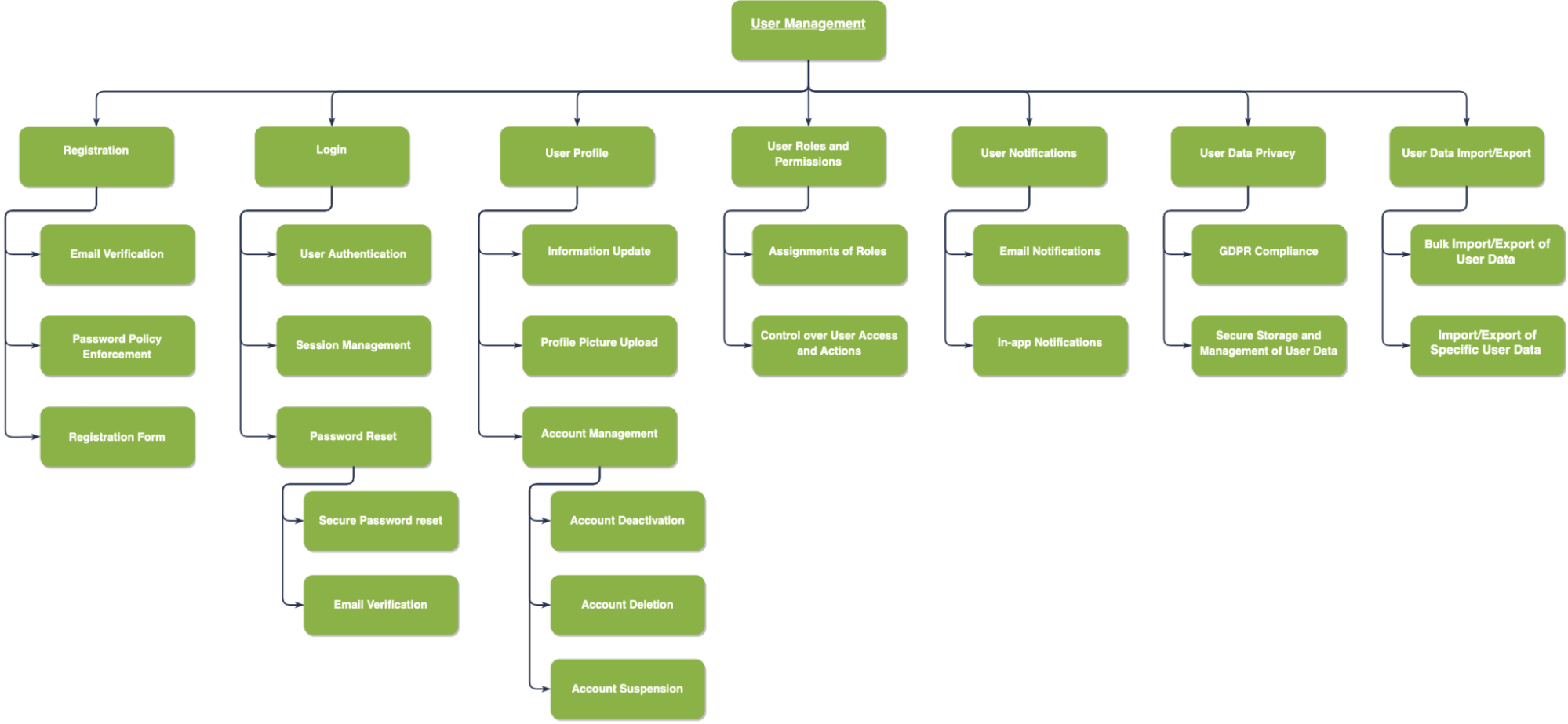
Figure 2 - Example of functional decomposition for user management feature
Another great example of functional decomposition in a project to develop a healthcare management system, the feature of appointment scheduling could be decomposed into functions such as viewing available appointment slots, booking an appointment, and canceling or rescheduling appointments.
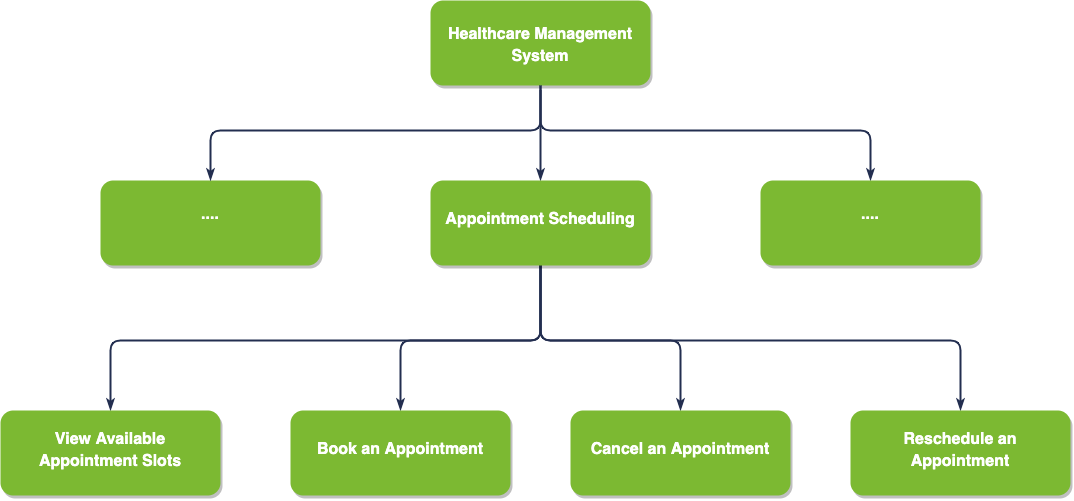
Figure 3 - Example of functional decomposition for healthcare management system
So, functional decomposition is a method that is often employed in a variety of sectors and businesses. Businesses may use it to simplify complicated procedures into smaller, more manageable activities and find opportunities for improvement. Businesses may boost productivity, decrease time and expense, and enhance overall performance by simplifying these operations.
Consumption aspects
Functional decomposition can be applied with the following usage considerations:
- Before beginning the functional decomposition process, it's crucial to have a clear understanding of the goals of the system.
- To make sure the system works as planned, it is crucial to define the boundaries of each component.
- To maintain the system over time, it is crucial to properly describe each component and how it interacts with other components.
- Decomposed components should be created to be autonomous and modular, preventing changes to one component from having an impact on the others.
- Avoid unnecessary decomposition since it might make the system more complicated and difficult to manage.
It is crucial to confirm that the decomposition correctly reflects the system's goals and needs and to periodically review and modify it as necessary.
|
Strengths |
Weaknesses |
|
Improved system structure and comprehension |
Excessive detail and rigidity |
|
Enhanced modularity and reuse |
Difficulty adapting to change |
|
Supports synchronous development |
Increased sophistication and integration challenges |
|
Enhanced error isolation and detection |
Reduced understanding of the system on a global scale |
|
Promotes incremental development |
Possibility of functional duplication and overlap |
Nevertheless, functional decomposition may be efficiently utilized to evaluate, create, and manage complex systems by taking utilization factors into account.
To sum up, functional decomposition is a helpful method in the design of complicated systems. Its hierarchical, modular form enables systems to be divided into more manageable, smaller pieces, making it simpler to comprehend, maintain, and grow.
Software Development Hub is a team of like-minded people with broad experience in IoT software development, web and mobile engineering. We provide clients with a full comprehensive custom development cycle, including architecture planning, business analysis for clients, UI/UX design, quality control, project management and support.
Categories
Share
Need a project estimate?
Drop us a line, and we provide you with a qualified consultation.