Cloud Service Models SaaS, PaaS, IaaS: How They Differ
The use of cloud servers, in contrast with "hard" ones, for solving corporate tasks has many advantages. The amounts of RAM and the number of processor cores to support the work can be adjusted. Based on the cloud, it is possible to apply any programs and systems; the access to data is 24 hours a day and does not depend on the user's location. Providers are totally responsible for system administration, software updates, and technical support. So if the owner of a company is planning to transfer business to the cloud, the only issue is choosing the right model.
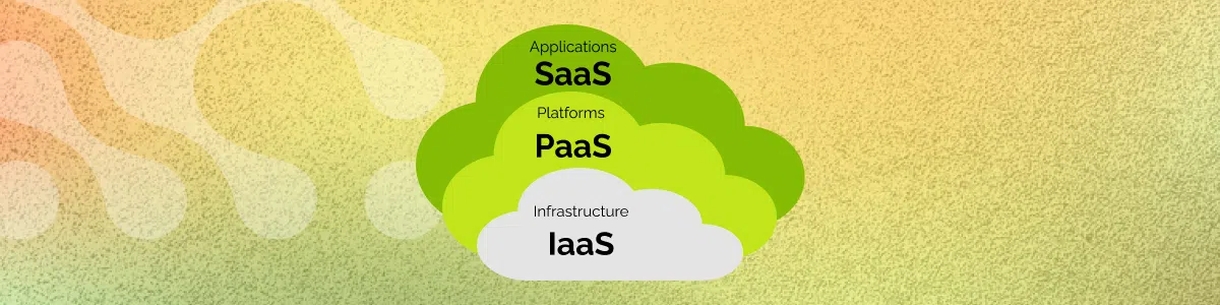
Among the cloud service models, the most popular are:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) – infrastructure as a service;
- Platform as f Service (PaaS) – platform as a service;
- Software as a Service (SaaS) – software as a service.
Below you will find the answers to what cloud service model to choose and what to pay attention to.
What IaaS is
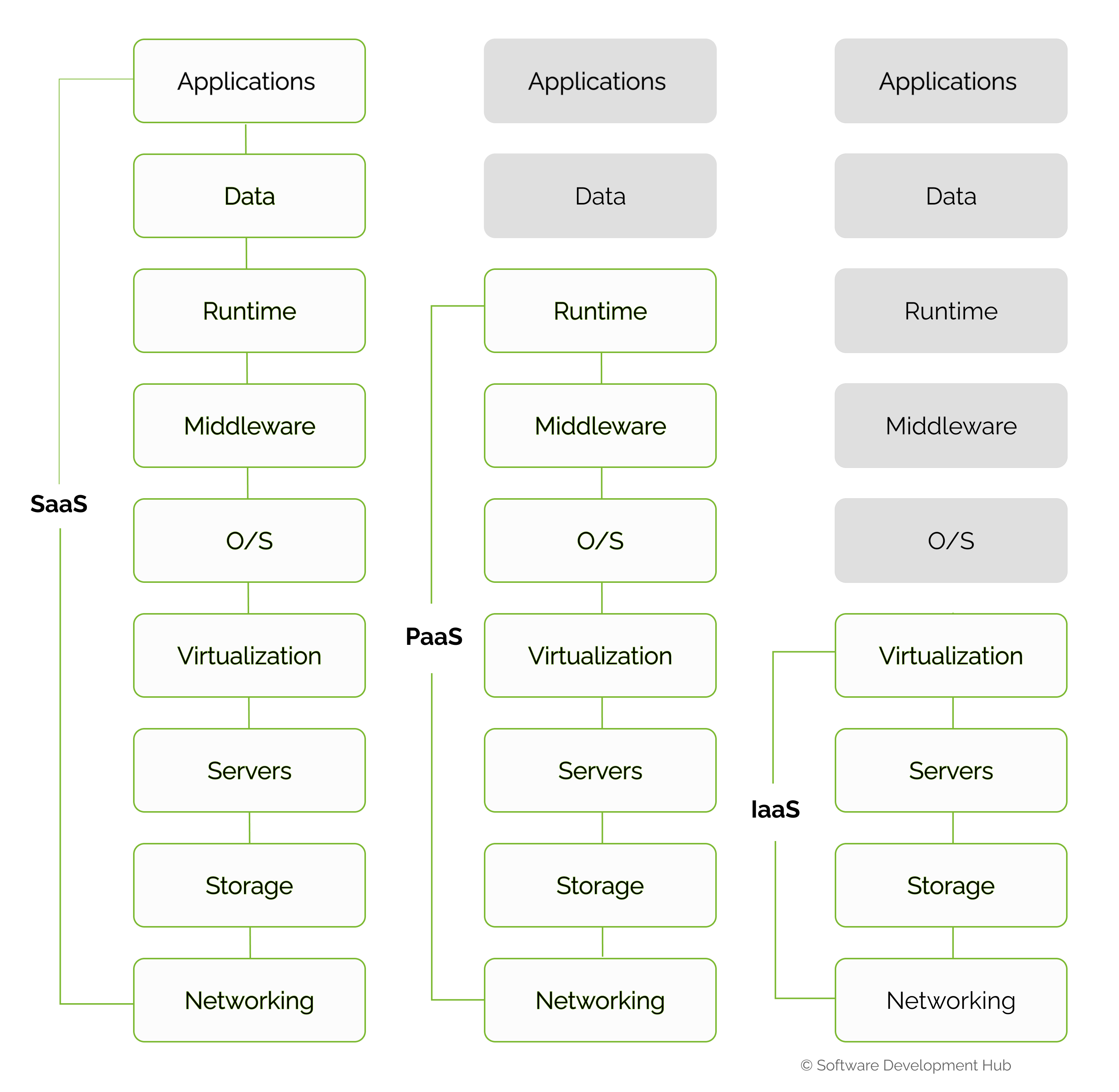
To understand the relationship between cloud service models, a pyramid with different levels of information management is depicted. The lowest level, the base, is the "Infrastructure as a service" model. Technically, IaaS is provided in the form of dedicated servers or virtual machines, disk storage, and a network connection tied to the Internet backbone. In other words, it is an IT infrastructure with a high level of automation and ability for scaling.
ISP services are billed on an operating expense (OpEx) model depending on the customer's use. This kind of subscription allows you to save on capital expenditure (CapEx), as you do not need to buy your own servers and other IT equipment.
How is the model IaaS useful? While applying it, it is possible to successfully scale IT resources, synchronizing the process with the level of workload and progress of projects. Providers offer services for preparing applications for work and applications for analysts. An important advantage is the provision of reliable protection and operation of the infrastructure in Tier III and Tier IV data centres with the redundancy of all systems. Achieving this level of redundancy in an On-Premises implementation is almost impossible or very expensive.
The peculiarity of IaaS is that only physical devices and a network connection to the Internet are given for rent. This feature distinguishes the model from the other two. The company's employees install the operating system and other software, so the provider is not responsible for their work. But suppose your team does not have such specialists. In that case, you can order an operating system and basic software from the provider, receiving additional service from the network engineer.
Access to cloud servers is provided through the control panel, which allows you to control the infrastructure and configure it according to the company's needs. The model provides ample opportunities for customization, especially if free code is available. Although the level of control over "hardware" and applications is significant too, it also has a downside — considerable costs for the wages of programmers and system administrators.
This data access format is ideal for online stores and trading platforms, whose owners seek to control the IT infrastructure without large investments in developing a data center. Representatives of small and large businesses use IaaS services. The most famous examples of its application are Amazon Web Services, Cisco Metacloud, and Microsoft Azure.
What PaaS is
The Platform-as-a-Service model is delivered as physical servers with pre-installed operating systems of the customer's choice. System software administration is unnecessary, but you can create and upload your own code or install a database.
The PaaS solution is often accompanied by an application deployment service. Which is much more convenient compared to IaaS model, where servers, operating system and applications still have to be configured.
At the same time, customization of the basic solution is available to the client: unique functions can be added without the intervention of the platform owner.
The model is optimal for companies with an existing IT infrastructure. Most famous examples are Windows Azure, Google App Engine, and OpenShift.
What SaaS is
Along with PaaS and IaaS, Software as a Service (SaaS) is one of the three main layers of cloud computing that allow businesses to redirect resources from spending on IT hardware, software and personnel to other needs.
The SaaS model is supposed to perform all redundancy and maintenance tasks by the vendor. These include cloud hosting of servers, installation of the operating system, and virtualization of backup tools and applications. In other words, the vendor develops, deploys and maintains e-commerce solutions. The client only has to pay the subscription fee or use the services for free, as the updates and technical support, they are the responsibility of the provider.
This option is convenient for representatives of small and medium-sized businesses, for whom it is important to configure the product as quickly as possible, avoiding paying expenses on a team of IT specialists. The users just access the cloud service through a web browser and manage the system from the admin panel.
By delegating issues of settings and maintenance to the vendor, the client frees up time for solving key tasks. However, such simplicity and convenience of management have a negative side, which is limited customization options: you can implement only those functions that the seller has planned.
Currently, software as a service generates roughly two-thirds of the cloud computing market revenue. And revenue growth in this area is not expected to slow significantly shortly. Gartner expects steady growth momentum in the SaaS segment as enterprises pursue different ways to enter the SaaS market and continue to break down large monolithic applications into component parts for more efficient DevOps processes.
SaaS is the basis for creating CRM, ERP, and ITSM systems. Among the typical examples of SaaS, implementations are Microsoft Office 365 and Google Workspace, which are used almost daily.
Conclusion
To sum up, it should be concluded from above, that the most flexible model is IaaS with a simple hardware redundancy process and the ability to increase computing resources when needed. The largest category of PaaS users is software developers who are vitally interested in optimization of the process of development, for example, in the team of developers in an IT company. The SaaS model is another level of service provision that makes it possible to save on software development and maintenance.
Categories
Share
Need a project estimate?
Drop us a line, and we provide you with a qualified consultation.